Classification of Matters with Examples
Matter is a term used for everything having
mass and volume. In this unit we will deal with types of matters. Pure
substance, elements, compounds, mixtures are subjects of this unit.

Properties of Pure Matters:
- They are homogeneous.
- They have specific physical properties like boiling point, density or freezing point.
- Temperature during phase change is constant
a) Elements: Element is the simplest matter which contains one type of atom. There are 109 known element in nature. We show elements with symbols like for iron we use "Fe".
Carbon "C"
Beryllium "Be"
b) Compounds: Two or more than two elements come together in specific amounts and form new matter that we call compound. Properties of compounds are totally different from elements comprising it. We show compounds with formulas like water H2O. Ions or molecules can produce compounds.
Salt "NaCl"
Ammonia "NH3"
Iron III Oxide "Fe2O3"
Properties of Compounds:
- All compounds are pure substances
- Smallest particle of compound is molecule including different types of atoms
a) Homogeneous Mixtures: All parts of mixture show same properties in homogeneous mixtures. We can call homogeneous mixtures as solutions. Salt water, sugar water, air are examples of homogeneous mixtures.
b) Heterogeneous Mixtures: Mixtures do not show same uniformity in all parts of it. In this types of mixtures, you can see different phases of matters. Water+Sand, milk, blood, soil are some common examples of heterogeneous mixtures.
Emulsion: Heterogeneous mixture including two different liquids. For example, oil-water, gasoline-water are emulsion examples.
Suspension: Heterogeneous mixture produced by one solid and one liquid matter.Sand-water, naphthalene-water are examples of suspension.
Colloids: are heterogeneous mixture type. Solute matters are homogeneously distributed in solvent however; we can see particles of solute with naked eye or microscope in colloids but, in solutions we can not see particles with microscope. Thus; colloids are assumed to be heterogeneous mixture.
Example: Which one of the following is heterogeneous mixture?
I. Coke
II. Sea Water
III. Water+Sand
IV. Natural Gas
Coke, sea water and natural gas are homogeneous mixture but water sand is heterogeneous mixture.
Differences between Compounds and Mixtures
- Ratio between matters forming compound is constant but ratio between matters forming mixture is variable.
- Matters forming compounds loose their properties but matters forming mixtures preserve their properties.
- We can decompose compounds with chemical methods but decompose mixtures with physical methods.
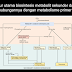
Elements, Compounds, Substances and Mixtures
In the study of science, it is very important to know that all solids are not the same, all liquids are not the same, and all gases are never the same. In addition to that, it is important to understand why all liquids are not the same, and why some are purer than others, in terms of their chemical makeup or compositions. This is why the classification of matter is important.
Matter can be classified into two categories: pure substances and mixtures. This classification is based on the internal composition of that matter. Using composition to describe matter is better than using its state, because the internal makeup makes matter unique, and not its phase or state. Example, water ( )
can be vapor, solid or the usual liquid. This means that
scientifically, it is not correct to say water is a liquid, even though
we all know that water is usually a liquid.
)
can be vapor, solid or the usual liquid. This means that
scientifically, it is not correct to say water is a liquid, even though
we all know that water is usually a liquid.

In a similar vein, classifying matter only according to its color, size, or weight is not enough because two identical objects can be of the same color, but their internal makeup may be different. Example, a glass of water from a lake may look and weigh the same as another identical glass of water from another lake — but it does not mean they are the same. They are all water, but the chemical compositions may be very different.
So, in this lesson, we shall see more about the classifications and the various ways and forms in which matter is made up, mixed up and if they can be separated at all.
First, it is very important to be very clear what some words mean. Let us begin with ‘elements' Elements
An element is a substance made from only one type of atom. For example, Oxygen ( ) is an element made up of ONLY oxygen atoms. To understand this better, let us see the how atoms behave.
) is an element made up of ONLY oxygen atoms. To understand this better, let us see the how atoms behave.

Every element is made up of atoms. Atoms are the smallest piece that can exist in an element. You will need to put millions of atoms together to get an element of about half millimeter in size. An atom is made up of ‘Electrons, Protons and Neutrons’.
The diagram on your left is an illustration of an atom. The center part is the nucleus.
Atoms in some elements do not join up with other atoms of the same element. An example is Helium. Helium atoms exist alone and can look like this:

Some atoms can also join up with other atoms of the same element. When two or more atoms join up, they form a molecule. Oxygen, ( ) is a molecule because it has two atoms joined together. An oxygen molecule looks like those in the diagram above.
) is a molecule because it has two atoms joined together. An oxygen molecule looks like those in the diagram above.
Elements are pure in nature. They may vary in size as long as the atoms joining to make its molecules are the same. As soon as a different atom joins (bonds), it ceases to be an element — it is now a compound.
Sometimes, atoms can join up with other atoms of other elements in chemical bonds. When that happens, a compound is formed. This means that a molecule can be made up of two atoms of the same element, OR can be made up more atoms of different elements.
Substances
A substance is simply matter with definite chemical composition and distinct properties. It is matter that is characterized by a constant composition in terms of its molecules, formulae and atoms, as well as physical properties such as density, refractive index, electric conductivity, melting point, and so on.
A substance can be an element or a compound but NOT a mixture. It can also be matter that exists in its pure form, usually called a pure substance. A few examples of substances include Water ( ), Hydrogen (
), Hydrogen ( ) and Neon (Ne).
) and Neon (Ne).
Other examples of chemical substances commonly seen in pure form are salt (sodium chloride), diamond (carbon) and gold.

The diagram above shows the classification of matter and where substances fit.
Substances cannot be separated into components by physical separation techniques. Some substances, like water, can be broken down into elements by a chemical reaction (to break chemical bonds). A substance can be solid, liquid, gas, or plasma.
Separating Mixtures
Mixtures come in many forms and phases. Most of them can be separated, and the kind of separation method depends on the kind of mixture it is. Below are some common separation methods:
 Paper Chromatography
Paper Chromatography
This method is often used in the food industry. It is used to identify chemicals (coloring agents) in foods or inks. For example, if a scientist wants to know how many substances are in a particular blob of ink, paper chromatography can be used. CLICK HERE to see how it works. Filtration
Filtration
This is a more common method of separating an insoluble solid from a liquid. An example of such a mixture is sand and water. Filtration is used in water treatment plants, where water from rivers is filtered to remove solid particles. CLICK HERE to see how it works. Evaporation
Evaporation
Evaporation is great for separating a mixture (solution) of a soluble solid and a solvent. The process involves heating the solution until the solvent evaporates (turns into gas) leaving behind the solid residue.
CLICK HERE to see an illustration of how it works. Simple distillation
Simple distillation
This method is best for separating a liquid from a solution. In a way, the concept is similar to evaporation, but in this case, the vapor is collected by condensation. For example, if you want to separate water from a salt solution, simple distillation would be great for this. CLICK HERE to see how it works. Fractional distillation
Fractional distillation
Similar to simple distillation, fractional distillation is best for separating a solution of two miscible liquids. (Miscible liquids are liquids that dissolve in each other). The Fractional method takes advantage of the different boiling points of the two liquids. CLICK HERE to see how it works. Magnetism
Magnetism
Magnetism is ideal for separating mixtures of two solids with one part having magnetic properties. Some metals like iron, nickel and cobalt have magnetic properties whiles gold, silver and aluminum do not. Magnetic elements are attracted to a magnet. CLICK HERE to see how it works.
 Separating funnel
Separating funnel
In this technique, two liquids that do not dissolve very well in each other (immiscible liquids) can be separated by taking advantage of their unequal density. A mixture of oil and water, for example, can be separated by this technique. CLICK HERE to see how it works.
Chemical Formulae
Very often in the study of science, you shall come across many elements and compounds that are represented by letters and numbers. These symbols are written in a definite way to tell us what the elements and compounds are made up of. They also tell us the various amounts of atoms in any substance.
Every element has a symbol. For example — Fe stands for Iron, O stands for Oxygen and C stands for carbon. It is very important to know the correct symbols of all the elements, because if they are not written properly, they change the entire meaning of it.
For example CO means one element of carbon and one element of oxygen together. This is Carbon Monoxide. It is NOT the same as Co, which is the symbol for cobalt.
The small numbers below the symbols tell us how many atoms of that element are in the molecule. 'O' means one atom of oxygen. means 2 atoms of hydrogen.
means 2 atoms of hydrogen.  , means two atoms of Hydrogen and one atom of oxygen. This is a water molecule.
, means two atoms of Hydrogen and one atom of oxygen. This is a water molecule.
When molecules react with other molecules, they form more complex compounds, with complex chemical formulae.
Here is an example:
The symbol for Sulphur is S, the symbol sodium is Na and that for Oxygen is O. If the atoms of these three elements react, they form a compound such as (Sodium sulphate) This compound has 2 atoms of Na, 1 atom of S and 4
atoms of O. Compounds with this formulae will be exactly the same
anywhere on earth because of its unique composition. The same can be
said of
(Sodium sulphate) This compound has 2 atoms of Na, 1 atom of S and 4
atoms of O. Compounds with this formulae will be exactly the same
anywhere on earth because of its unique composition. The same can be
said of  (water molecule). If we use the chemical formulae
(water molecule). If we use the chemical formulae  ,
it will be the same anywhere on earth, BUT if we say water, it will not
be the same anywhere on earth because water is generic and may contain
other atoms of other elements in it.
,
it will be the same anywhere on earth, BUT if we say water, it will not
be the same anywhere on earth because water is generic and may contain
other atoms of other elements in it.


Why the classification is very important in addition to knowing that all solids are not the same, all liquids are not the same and all gases are not the same?
BalasHapusBecause with the classification we can know what is solids, liquids, and gases, the difference of each and the example
HapusGive examples of molecules react with other molecules to form a complex compound
BalasHapusMetal ions in water solvent form complex [M (H2O) 6] n +. At the moment into the solution added unstained monodentate ligand then the reaction occurs:
Hapus[M (H2O) 6] n + + L ® [M (H2O) 5L] n + + H2O
The reaction continues for the six substituted H2Os and the complex [ML6] n + is produced. When the added ligand is a bidentate ligand the reaction consists of three stages. At each stage two molecules of H2O are substituted by a bidentate ligand until at the end of the reaction the [ML3] n + complex is obtained.
Complex with one central metal ion is known as a single nucleus complex (mononuclear).
Substances cannot be separated into components by physical separation techniques, so give me an example substance can be separation with physical separation techniques?
BalasHapusComposite components of such a mixture may be separated by the physical properties of their constituents. There are two kinds of mixtures, namely homogeneous mixtures and heterogeneous mixtures. Therefore if a mixture is not suitable to eat can not be separated
Hapuswhy a substances can not be separated into components by physical separation techniques?
BalasHapusComposite components of such a mixture may be separated by the physical properties of their constituents. There are two kinds of mixtures, namely homogeneous mixtures and heterogeneous mixtures. Therefore if a mixture is not suitable to eat can not be separated
HapusWhy protons and neutrons don't have the same charge ?
BalasHapusSurely protons and neutrons are different from the sense alone is different as well from the amount, if you want to find the value of neutrons then the number of no mass is reduced by the number of protons
HapusCan you explain,what is the purpose of the statement "Ratio between matters forming compound is constant but ratio between matters forming mixture is variable?"
BalasHapusThe ratio between the things that make up the compound is constant but the ratio between the things that make up the mixture is varied and
HapusThe things that make up the compounds lose their properties but the things that make up the mixture preserve their properties.
We can decompose the compound by chemical method but describe the mixture by physical method.
What is the difference between protons, neutrons, and electrons?
BalasHapusThe definition of Proton is as follows: Definition Proton is a positively charged electrical charge carrier. Electrons are negatively charged particles. Electrons are located in atoms (bound to atomic nuclei) and cause chemical properties. In the metal, electrons are ebas (unbound atoms) so they can conduct an electric current. In semiconductors, the flow of electrons can be adjusted so that diode, transistor and others can be made.
HapusNeutrons are non-charged (neutral) subatomic particles and have a mass of 940 MeV / c² (1.6749 × 10-27 kg, slightly heavier than protons.) The rotation is ½
why substance different from matter?
BalasHapusHere it is explained that matter and matter are the same from the sense that the Matter is everything that occupies space and has mass. While Substance is something that occupies space and has mass. Means that matter and matter are no different
HapusCould u give me some example about the oxygen feature as we know it's easy to tied with the another elements?
BalasHapusSo the oxygen cycle is the process of exchanging oxygen on this earth that goes on and on continuously endlessly. During the early evolution of the earth, oxygen liberated from H2O vapor by UV radiation. It accumulates in the atmosphere as hydrogen escapes the Earth's atmosphere. With the advent of plant life, photosynthesis is also a source of oxygen. Oxygen is also released as organic carbon in CHO, and gets dimakamkandi sediment.
HapusThis cycle illustrates the exchange of oxygen between the forms of gas O2
Which are present with large amounts in the atmosphere, and chemically bonded oxygen in CO2,H2O dan organic materials. This cycle is closely related to other cycle elements, especially with the carbon cycle. The oxygen element becomes chemically bonded through various energy-generating processes, especially in the changes and metabolites in the organism. Oxygen is released from photosynthetic reactions
How to distinguish pure substances with mixed substances and give examples?
BalasHapusPure substance is a substance that contains only one kind of constituent substance. By means of physics, pure substances can not be broken down into other simpler substances. Examples of pure substances are 24 carat gold, distilled water or aquades, and pure iron. Mixture is a substance that contains two or more kinds of constituents. Other examples of the mixture that surrounds us, such as atmosphere, bronze, brass, sea water, and soil.
HapusHay nadia, Give me an explanation and examples of Elements belonging to a metaloid element and a liquid element at room temperature
BalasHapusMetals are unique toxicants. Metals are found and settled in nature, but their chemical forms may change as a result of physicochemical, biological or human activity.
HapusMetal is a natural element that can be obtained from the sea, erosion of mine rocks, volcanism and so on. Generally metals in nature are found in the form of compounds with other elements, very rarely found in a single element. This element in the condition of room temperature is not always in the form of solid but there is a liquid, for example mercury (Hg). In aquatic bodies, metals are generally present in the form of ions, either as ion pairs or in the form of single ions. While in the atmospheric layer, the metal is found in particulate form, where the elements of the metal come to fly with dust in the atmosphere.
Heavy metals are natural components of the environment that get excessive attention due to being added to the soil in increasing amounts and the danger that may arise. Heavy metals refer to metals having a specific gravity higher than 5 or 6 g / cm 3. But in reality in terms of this heavy metal, also incorporated metalloid elements that have dangerous properties such as heavy metals so that the total number of approximately 40 species. Some of the toxic heavy metals are As, Cd. Cr, Cu, Pb, Hg, Ni, and Zn.
Whether the same atoms can combine to form compounds?
BalasHapusCan be because the compound is a single substance consisting of several elements that interconnect each other. Compounds are formed from at least 2 different elements. Although they are formed from different substances, they are still called single substances, because the properties of the constituents they form can not be found in the compound. And some elements are A group of atoms that have the same number of protons at their core. This number is called the elemental atom number. The element is also defined as a single substance that can no longer be divided into smaller parts.
Hapus