Rendement
In chemistry, the chemical yield, the yield of the
reaction, or only the rendement refers to the amount of reaction product
produced in the chemical reaction. [1] Absolute rendement can be written as
weight in grams or in moles (molar yield). The relative yield used as a
calculation of the effectiveness of the procedure is calculated by dividing the
amount of product obtained in moles by the theoretical yield in moles:
To obtain a percentage yield, multiply the
fractional yield by 100%.
One or more reactants
in chemical reactions are often used redundantly. The theoretical rendement is
calculated based on the number of moles of the limiting reagent. For this
calculation, it is usually assumed that there is only one reaction involved.
The ideal chemical
yield value (theoretical rendement) is 100%, a value highly unlikely to be
achieved in its practice. Calculate the percentage of rendement that is by
using the following equations percent rendemen = weight yield / weight of yield
divided by the sample weight multiplied by 100%
Calculating Rendemen Value
Rendement
is the ratio of the amount (quantity) of oil produced from the extraction of
aromatic plants. Rendemen use percent unit (%). The higher the yield value
indicates that the value of the oil produced is more benyak. Increasing the
yield or the ratio of the amount of oil produced can be done with two
approaches, First, the process of cultivation. Second, the process of
making oil The quality of the oil produced is usually inversely proportional to
the number of rendaments produced. The higher the resulting rendamen the lower
the quality obtained. The formula for calculating the following rendamen:
Each plant has a different rendament value, below can be seen examples
of some redamen values: Table Rendamen Varieties Some Types of Asiri Plant
Various kinds of chemical reactions or types of chemical reactions consist of:
coalescing
reactions, decomposition reactions, change reactions and metathesis reactions,
combustion reactions. Check out the full review below. Ironing is one
type of chemical reaction Chemical reactions can be observed from changes, such
as changes in color, changes in shape, and the main thing is the change of
substances accompanied by changes in energy in the form of heat. Chemical reactions
are the key to chemistry. By reacting a substance means we turn the substance
into another substance, both the nature and the form. Thus, if we expect a
substance that has certain characteristics, we must try to find raw materials
that when reacted with certain substances produce substances that we expect.
Chemists are trying to create new materials that are very useful for the
benefit of mankind. The following will explain some types of chemical reaki
that can be done dilaboratorium. TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS By knowing some
properties or types of reactions, we can understand the chemical reactions more
easily. Generally, chemical reactions are classified by type as follows: 1.
Reaction of merging 2. Decomposition reaction 3. Reaction of change (single
exchange reaction) 4. Metathesis reaction (multiple exchange reaction) 1.
MUTUAL REACTIONS The merging reaction is a reaction in which two substances
merge to form a third substance. The simplest case is when two elements react
to form a compound. For example sodium metal reacts with chlorine gas to form
sodium chloride. The equation of the reaction:
2Na
(s) + Cl2 (g) → 2NaCl (s)
Other examples are the reaction between white phosphor and chlorine gas. In limited chlorine amounts,
phosphorus reacts to form phosphorus trichloride, PCl3, a colorless liquid.
P4 (s) + 6Cl2 (g) → 4PCl3 (l)
If the chlorine is excessively available, the resulting phosphorus compound is phosphorus pentachloride,
PCl5, a white solid.
P4 (s) + 10Cl2 (g) → 4PCl5 (s)
Other merging reactions involve the compound as reagents. For example: phosphorus trichloride reacts
with chlorine gas to form phosphorus pentachloride. The equation of the reaction:
PCl3 (l) + Cl2 (g) → PCl5 (s)
2. REACTION OF PUNISHMENT
The decomposition reaction is a reaction when a single compound reacts to form two or more
substances. Usually this reaction requires a rise in temperature for the decomposable compound by increasing
the temperature eg KclO3. This compound when heated will decompose into KCl and oxygen gas. The equation of the reaction:
KClO3 (s) → 2KCl (s) + 3O2 (g)
Decomposition of potassium chlorate is commonly used to generate laboratory oxygen gas.
The decomposition reaction is commonly applied in limestone processing in the area of West Java cipatat. Limestone,
CaCO3 extracts that can be used as building materials need to be further processed into tohor, CaO. The processing of limestone
is done by way of roasting limestone in the stove. The chemical equations are:
CaCO3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
In this reaction, a single compound is broken down into two different substances.
3. REACTION OF EXCHANGE
Reaction of a change or also called a single exchange reaction is the reaction in which an element reacts with a compound to replace
the element contained in the compound. For example, if the copper metal plate is immersed in a silver nitrate solution, a silver metal crystalline
is produced. The equation of the reaction is:
Cu (s) + 2AgNO3 (aq) → 2Ag (s) + Cu (NO3) 2 (aq)
Copper replaces the silver contained in silver nitrate, producing a solution of copper nitrate and silver metal. If the logamseng plate is
immersed in a blue sulfate copper solution, then on the surface of the zinc metal there will be a red copper deposit, and the blue color of the solution
slowly fades. This shows that zinc reacts with copper sulfate to produce copper metal and a colorless zinc sulfate solution.
4. METATESIS REACTION
The reaction of metathesis or multiple exchange reactions is a reaction involving the exchange of parts of the reactants. If the reagents are
ionic compounds in solution form, the exchange portion is the cation and anion of the compound. For example a colorless potassium iodide solution is
mixed with lead (II) nitrate solution which is also colorless. The ions in the solution react to form a yellow precipitate of the lead (II) iodide compound.
The equation of the reaction:
2KI (aq) + Pb (NO3) 2 (aq) → 2KNO3 (aq) + PbI2 (s)
Iodide ions in the potassium iodide solution exchange with nitrate ions from lead (II) nitrate solution, yield a colorless potassium nitrate solution and a
yellow i (y) iodide lead solid, as PbI2. The acid and base reaction that produces salt, is also considered a metathesis reaction. For
example the reaction between hydrochloric acid, HCl (aq) and sodium hydroxide (aq), the equation of the reaction:
HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (l)
The acid-base reaction is also called the neutralization reaction, because it occurs the inclusion of the H + charge by the electrically neutral (H2O)
water-formed OH. The salt of NaCl formed remains in solution as its ions.
COMBUSTION REACTIONS
The reactions we consider so far can be characterized as reactor reactions of atoms. However, we need to add another kind of reaction that is
the combustion reaction, which is characterized by the fact that one of its reactants is oxygen. The combustion reaction is the reaction of a substance with
oxygen, usually reacting rapidly with the release of heat forming a flame. If carbon compounds are burned in oxygen or air will form carbon
dioxide and water vapor when the combustion is complete. However, if incomplete combustion (lack of oxygen) will form carbon monoxide
gas, or may be formed carbon black (soot). Some examples of combustion of carbon compounds:
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) → CO¬¬2 (g) + 2H2O (g)
2CH3OH (l) + 3O2 (g) → 2CO2 (g) + 4H2O (g)
C4H10 (g) + 13O2 (g) → 8CO2 (g) + 10H2O (g)
Ironing, although not commonly considered as combustion, is essentially a combustion reaction, because there is a reaction between iron and oxygen accompanied
by the release of energy. The iron-cellification reactions are in fact very complex involving water molecules, but we can write the karate in the form of a net reaction,
which is as follows:
4Fe (s) + 3O2 (g) + nH2O (l) → 2Fe2O3.nH2O (s)
Thus writing about various chemical reactions. If any feedback, suggestions or questions, please comment yes. May be useful….
Source:
Sunarya, Y. (2003). Chemical Association 2. Alkemi Grafisindo Press: Bandung



How if% rendement is small than 50%? What does it mean
BalasHapusThe ideal or theoretical result of a chemical reaction is 100%. According to Vogel's Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry, yielding about 100% is called quantitative, yields above 90% are called very good, yields above 80% are excellent, results above 70% are good, results are over 50% fair, and the results are below 40% are called poor.
HapusReaction of a change or also called a single exchange reaction is the reaction in which an element reacts with a compound to replace. Give me more example and how to do it!
BalasHapusIf the copper metal plate is immersed in a silver nitrate solution, a crystalline silver metal is produced. The equation of the reaction is:
HapusCu (s) + 2AgNO3 (aq) → 2Ag (s) + Cu (NO3) 2 (aq)
Copper replaces the silver contained in silver nitrate, producing a solution of copper nitrate and silver metal.
If the logamseng plate is immersed in a blue copper sulphate solution, then on the surface of the zinc metal there will be a red copper deposit, and the blue color of the solution slowly fades. This shows that zinc reacts with copper sulfate to produce copper metal and a colorless zinc sulfate solution.
What is the difference between real yield and theoretical rendement?
BalasHapusTo obtain a percentage yield, multiply the fractional yield by 100%.
HapusOne or more reactants in chemical reactions are often used redundantly. The theoretical rendement is calculated based on the number of moles of the limiting reagent. For this calculation, it is usually assumed that there is only one reaction involved.
The ideal chemical yield value (theoretical rendement) is 100%, a value highly unlikely to be achieved in its practice. Calculate the percentage of rendement that is by using the following equations percent rendemen = weight yield / weight of yield divided by the sample weight multiplied by 100%
For what is the process of neutralization?
BalasHapusNeutralization is a process for separating free fatty acids from oils or fats by reacting free fatty acids with bases or other reactants to form soap (soap stock). Separation of free fatty acids can also be carried out by distillation known as de-acidification. The goal of the neutralization process is to remove free fatty acids (FFAs) which can cause a rancid odor.
HapusIf both ways can not be done is there any other way that can be done to increase the yield of the amount of oil produced?
BalasHapusThere is like the Petroleum Distillation
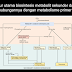
HapusCrude oil contains about 500 types of hydrocarbons with the number of C-1 to C-50 atoms. The processing of petroleum is carried out by a multilevel distillation, in which crude oil is separated into groups of similar boiling points. This is done because the boiling point of hydrocarbons increases with the increase of carbon atoms (C) in the molecule. Initially the crude oil is heated at a temperature of about 400 ° C. Once heated and then flowed to the fractionation / distillation tube.
Distillation tower
In this tower occurs the process of distillation (distillation). That is the process of separating the solution by using heat as a separator. The basic principle of stratified distillation is the difference in the boiling point between the crude oil fractions. If the difference in the boiling point does not vary greatly then the distillation can not be applied. The hydrocarbon having the lowest boiling point will be separated first, followed by a hydrocarbon having a higher boiling point.
Figure 1 The distillation tower
Distillation of Petroleum Fractionation
Although the composition is complex, there is an easy way to separate the components based on their different boiling point values, called distillation processes. Distillation is the separation of petroleum fractions based on their different boiling points. The diagram of the separation of petroleum components by distillation is shown by the image below:
Petroleum distillation diagram
Crude oil or crude oil before entering into the fractionation column (separator column) is first heated in a pipe stream in the furnace (furnace) up to a temperature of ± 350 ° C. The heated crude oil then enters the fractionation column on the flash chamber (usually on the bottom third of the fractionation column). To maintain the temperature and pressure in the column then assisted heating with steam (hot water vapor and high pressure).
Because of the difference in the boiling point of each hydrocarbon component, the components will be separated by themselves, wherein the light hydrocarbon will be at the top of the column followed by a heavier fraction below. In the tray (bulkhead in the column) the components will be collected according to their respective fractions.
At each level or fraction collected then pumped out the column, cooled in a cooling bath, then accommodated in the tank of each product. This product can not be directly used, because it must be added additive (adder).
Rendemen search for 100% value but the results obtained will not reach pratiknya?
BalasHapusBecause what is known in the question is not a hundred then the result is not the same as 100, here is an example: Mr.O have 50 mangoes, and 10 berries was given to his first child, the question is what percentage of the remaining mango Mr.O? Must have guessed how much the rest, here are the details:
BalasHapus10/50 x 100 = 20%
10 is the number who want sought percentannya, while 50 is the number that shows all the parts or 100%. If it is minimized or regular fractions (100% it = 1) so if 0.2 = 20%.